About VCR gas pressure regulator and its features!
1. What gases the VCR gas pressure regulator is suitable for?
VCR gas pressure regulators are suitable for hazardous and ultra-high purity gases.
2. What are the hazardous gases for which the VCR gas pressure regulator is suitable?

Common dangerous gases and related information are:
Ammonia (NH3): Ammonia is a common chemical widely used in agricultural fertilizers, refrigerants, cleaning agents and industrial processes.
Chlorine (Cl2): Chlorine is a commonly used chemical for disinfection, bleaching, water treatment and the manufacture of other chemicals.
Carbon dioxide (CO2): Carbon dioxide is a common gas used as a carbonating agent in the food and beverage industry, as well as in welding, firefighting and other industrial applications.
Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN): Hydrogen cyanide is a highly toxic gas used in metallurgy, organic synthesis and pesticide manufacturing.
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S): Hydrogen sulfide is a highly malodorous and toxic gas commonly used in the oil and gas industry and other industrial processes.
Hydrogen Chloride (HCl): Hydrogen Chloride is a gas with an irritating odor and is commonly used in the manufacture of chemicals, cleaning metals, and regulating pH levels.
Nitrogen (N2): Nitrogen is an inert gas commonly used to protect and inert reaction environments, as well as for gas containment and pressure testing.
Oxygen (O2): Oxygen is an essential gas commonly used in the medical industry, gas cutting, welding and combustion processes.
3. Characteristics of VCR gas pressure regulator?
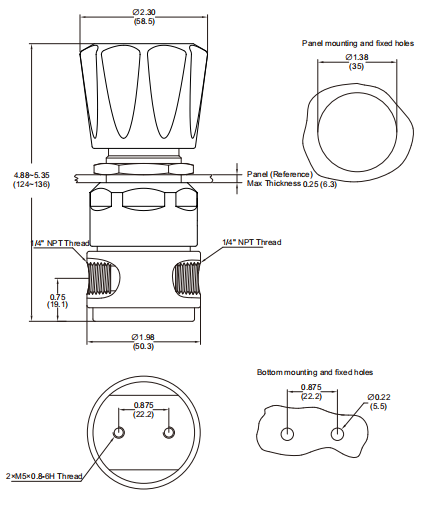
HIGH ACCURACY REGULATION: The VCR Gas Pressure Regulator utilizes a precise regulation mechanism that provides highly accurate gas pressure regulation. This makes it useful in applications where accurate control of gas flow and pressure is required, such as in laboratory research, precision manufacturing and gas analysis.
Reliability and Stability: Designed for long-term stable gas regulation, VCR gas pressure regulators are capable of providing reliable performance under varying operating conditions. They are typically constructed using high quality materials and workmanship to ensure reliable operation over long periods of time and to minimize the risk of leakage and failure.
Multiple Connection Options: VCR gas pressure regulators are typically available with a variety of connection options to accommodate different gas piping and system requirements. Common connection options include VCR metal-sealed fittings, flanged connections, and threaded connections, making the installation and integration of the regulator flexible and easy.
Wide range of adjustability: VCR gas pressure regulators typically have a wide range of adjustability to accommodate different pressure requirements. Whether high or low pressure regulation is required, they provide the appropriate solution.
Safety features: VCR gas pressure regulators are often equipped with a variety of safety features to ensure the safe operation of the system. These features may include over-pressure protection, over-current protection, over-temperature protection and leak detection to minimize the risk of potential hazards and accidents.
Adjustability: VCR gas pressure regulators are typically adjustable, allowing the user to set and adjust the pressure to specific needs. This adjustability makes the regulator suitable for different application scenarios and process requirements.
4. The environment in which the VCR gas pressure regulator is assembled?
VCR gas pressure regulators are assembled in clean rooms to ensure cleanliness and to help maintain the integrity and performance of the VCR gas pressure regulator.
5. How VCR Gas Pressure Regulators Work?

Gas Inlet to Regulator: Gas enters the VCR gas pressure regulator through a connecting line. The inlet is usually connected to a gas source.
Pressure Sensing: Inside the regulator there is a pressure sensing element, usually a spring or a diaphragm. As the gas enters the regulator, the pressure sensing element is subjected to the gas pressure and generates a corresponding force.
Balancing of Forces: The force of the pressure sensing element is balanced against a regulating mechanism inside the regulator. This mechanism usually consists of a regulating valve and spool.
Regulating Valve Operation: Depending on the force of the pressure sensing element, the regulating valve will open or close accordingly to adjust the pressure of the gas flowing through the system. When the force of the pressure sensing element increases, the regulating valve closes, decreasing the gas flow and thus lowering the system pressure. Conversely, when the force on the pressure sensing element decreases, the regulating valve opens, increasing the gas flow and raising the system pressure.
Pressure Stabilization: By continually adjusting the valve opening, the VCR Gas Pressure Regulator maintains a steady pressure of gas flowing through the system. The regulator will adjust in real time as needed to ensure that the gas pressure in the system remains within a predetermined range.
 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 NL
NL
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 ID
ID
 VI
VI
 MT
MT
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 AZ
AZ